
Native Linux Execution for Android Apps

Native Linux Execution for Android Apps
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
Key Takeaways
- Waydroid is the best option for running Android apps on Linux systems using Wayland display server, such as newer versions of Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, or Arch.
- Creating an Android virtual machine using the open-source Android x86 project is a simple way to run Android apps on your Linux PC.
- Android Studio is primarily for developers but can be used to create a personal Android Virtual Device (AVD) for running Android apps on Linux.
While you might not be able to install Bluestacks, there are a few fantastic methods you can use to run Android apps and games on your Linux PC. You can create an Android virtual machine, install Waydroid, emulate with Android Studio, or even purchase Genymotion and enjoy a highly supported emulation experience.
What Is the Best Option for Running Android Apps on Linux?
You have quite a few methods to choose from to run Android apps and games on Linux. As mentioned before, creating an Android virtual machine, using Android Studio, installing Waydroid, and purchasing Genymotion are just a few of your options.
You’ll need to consider your own Linux setup and desired emulation experience to determine which option is best. Here’s a basic overview:
- Waydroid: This application is the best option for Linux systems using the Wayland display server. If you use a newer version of Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, or Arch, you’re probably using Wayland.
- Create an Android virtual machine: If you want to run an extremely simple Android system, you can use the open-source Android x86 project by installing it as a virtual machine on your PC.
- Use Android Studio: Android Studio is primarily geared towards developers, but you can also use it to create a personal Android Virtual Device (AVD). This isn’t the best method due to the inherent learning curve, however.
- Genymotion: This pay-to-use application offers a convenient way to run Android virtual devices. It’s particularly good for developers, but you may also enjoy it if you want the level of support that a premium application offers.
Many guides recommend installing Anbox—but unfortunately, this application was deprecated in February 2023. You’ll need to find a supported alternative if you want to run Android apps.
1. Use Waydroid to Play Android Games
Overall, the best method to run Android games in light of the deprecation of Anbox is using Waydroid. Before you can start using Waydroid, though, it’s important to check whether you’re running the requisite display server: Wayland.
You can check whether your system runs Wayland by opening the terminal and entering the following to print your session type:
echo $XDG_SESSION_TYPE
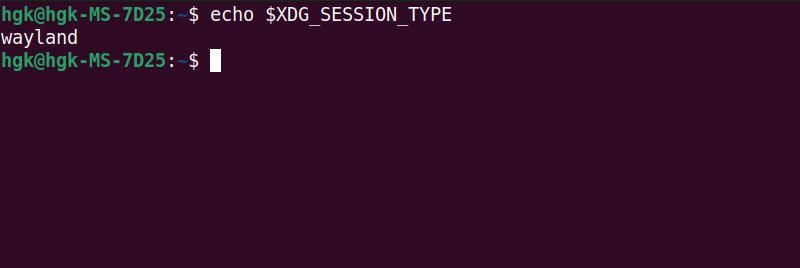
If your system runs the Xorg display server, you’ll need to switch from Xorg to Wayland before you can install Waydroid.
On Ubuntu, you can switch to Wayland by logging out of your user account and clicking theGear icon on the login screen. When the drop-down list of display options appears, clickUbuntu to switch out of the Ubuntu on Xorg configuration.
Next, you should update your system’s package list. This will ensure that the software packages you install are all completely up-to-date. Enter the following to update the package list:
sudo apt update
You’ll also need to follow theWaydroid installation instructions for your specific Linux distribution. On Ubuntu, Debian, and their derivatives, you can install Waydroid by entering the following in the terminal to install prerequisites, add the Waydroid repository to your system, and install Waydroid:
sudo apt install curl ca-certificates -y curl https://repo.waydro.id | sudo bash sudo apt install waydroid -y
Once Waydroid is installed, you’ll need to take a few steps to initialize the program. You’ll need to start the Waydroid container and enable its GUI (Graphical User Interface). You can accomplish this by entering:
sudo waydroid container start waydroid show-full-ui
Finally, you’re ready to install Android apps on your PC. You’ll need tonavigate to a reputable website like APKMirror or APKPure to download the APK file for each app you want to install. Once you’ve downloaded your APKs, enter the following to install the app on your system:
waydroid app install appname.apk
Wait for the app to install. Once the installation process is complete, you can run the Android app by selecting it through the Waydroid GUI, launching it through your desktop application menu, or launching it from the terminal with:
waydroid app launch appname
2. Create an Android Virtual Machine
If you’re comfortable creating a virtual machine, one of the best ways to run Android apps and games on your Linux PC is to virtualize an Android x86 system. To start, you’ll need to download the Android x86 ISO image.
You’ll also need to download your virtualization software of choice—in this case, we’ll use VirtualBox. This software is suitable for Ubuntu, Debian, openSUSE, and derivative distributions.
Download: Android x86
Download: VirtualBox
Download the appropriate package for your Linux distribution, then install it from the terminal.
On Ubuntu and Debian-based distros, right-click on the file and selectOpen with another application . SelectSoftware Install from the dropdown list, and finally, clickInstall . Wait for VirtualBox to finish installing on your system.
Once it’s finished installing, open VirtualBox. Click on theNew button to create a new virtual machine, setting the following configurations:
- Type: Linux
- Version: Linux 2.6 / 3.x / 4.x (32-bit or 64-bit depends on which version of Android x86 you installed)
- RAM: 2GB (2048MB) minimum, more if possible
- HDD file type: VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)
- Storage: Dynamically allocated
- HDD: 8GB (8192MB) minimum, more if possible
After you’ve created the new virtual machine, you’ll still need to configure a few more settings. Select your new virtual machine from the list of VMs and click onSettings . InSystem > Processor , allocate two or more CPU cores.
InSystem > Acceleration , select KVM as the paravirtualization interface. In theDisplay > Screen tab, you’ll need to change the Graphics Controller setting toVBoxSVGA .
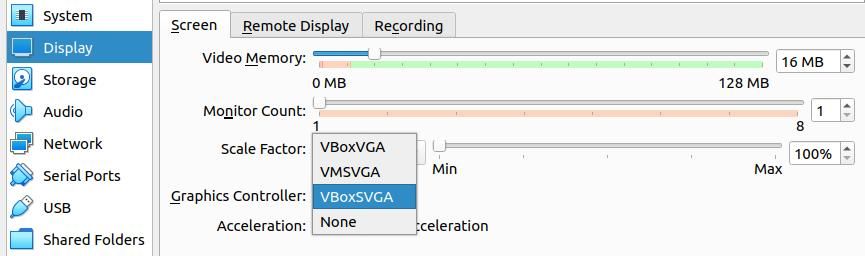
Last but not least, you’ll need to install the Android x86 image. Navigate to theStorage tab and selectEmpty from the list of storage devices. Next, click on theblue disc icon to the right of theOptical Drive setting and selectChoose a disk file from the dropdown menu. Select your Android x86 ISO from the Files interface that appears. Finally, close the settings menu and clickStart to boot your Android VM.
As prompts appear on the new virtual machine, clickAdvanced Options , selectAuto_Installation from the advanced options list, and then clickYes to confirm the auto installation.
Once the installation process is complete, you can configure and install apps on your new Android virtual machine.
3. Use Android Studio for Seamless Gaming
While Android Studio is primarily geared towards developers, it can be an excellent option for emulation if you aren’t interested in using Waydroid or an Android x86 virtual machine. Afterinstalling Android Studio , you’ll need to create an Android Virtual Device (AVD) using the officialAndroid Developer’s guide and then install your chosen APK on theAndroid Emulator.
4. Run Android Apps on Linux With Genymotion
It’s worth considering applications like Waydroid and even tried-and-true virtual machines before you purchase Genymotion. In most cases, it’s possible to accomplish anything you want on your Linux PC without purchasing proprietary applications.
If you choose to purchase Genymotion, however, you’ll be enthused with the ease of use and convenience that this application offers.
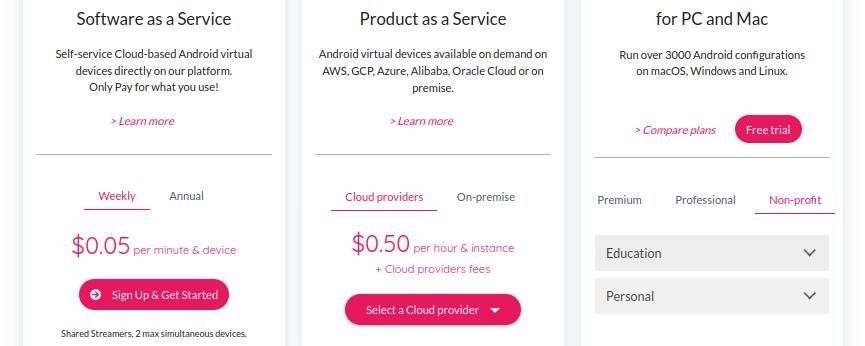
To start, you’ll need to purchase the right Genymotion plan. Genymotion offers a free plan for personal use, but any technical support requests beyond issues with installation and first run will be rejected—and you won’t be able to use features like Android 13, camera and media widget features, and quick boot.
If you’re a current student or teacher, you can use your school ID to purchase full-featured Genymotion for $49 per year.
Once you’ve downloaded the Genymotion BIN file, you can install it with QEMU or VirtualBox usingGenymotion’s official installation guide.
Enjoy Using Android Apps and Games on Your Linux System
With the deprecation of Anbox, it’s easy to wonder if any easy methods to run Android apps on Linux systems remain. Luckily, Waydroid, Android x86, Android Studio, and Genymotion all offer distinct and easy ways to run Android apps.
Once you’ve chosen which software to use, you’ll be amazed at just how convenient and seamless using these apps is.
Also read:
- [New] Dive Into Video Production Mastering Green Screens on YT for 2024
- [New] Expert Picks 17 Superior Apps for Quick Image Sharpening
- [New] Hexa-Drone Elite Collection - The Finest Ten for 2024
- [New] Non-Sport Spectacles in the Top Ten Front Rows for 2024
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Channel Marketing Making a Trailer that Sells More
- [Updated] In 2024, The Ultimate Tutorial for Musical Instagram Video Posts
- All Must-Knows to Use Fake GPS GO Location Spoofer On Vivo Y36i | Dr.fone
- Digital Entertainment: Unpacking 9 Favorable and Foe Factors
- Efficient Control of Xbox Live Gold on XS
- Free Games That Don't Cost a Dime: Our Top 6
- In 2024, How To Remove or Bypass Knox Enrollment Service On Samsung Galaxy F14 5G
- Masterclass on Netgear Orbi: The Ultimate Leader in Today's Wi-Fi Solutions
- Savvy Spending on Inexpensive Gamer Tech Boards
- Steps to Overcome Steam Content Unavailable Error
- Streamlining File Sharing in Steam for Windows
- Title: Native Linux Execution for Android Apps
- Author: William
- Created at : 2025-02-25 17:40:19
- Updated at : 2025-03-02 20:21:12
- Link: https://games-able.techidaily.com/native-linux-execution-for-android-apps/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.