Enhance Your Gameplay with the Seamless Magic of Nvidia G-Sync

Enhance Your Gameplay with the Seamless Magic of Nvidia G-Sync
Quick Links
- What Is Nvidia G-Sync and How Does It Affect Your Games?
- Different Types of G-Sync Explained
- Hardware Requirements for G-Sync and G-Sync Ultimate
- G-Sync vs. FreeSync
- Should You Buy G-Sync-Compatible Hardware?
Key Takeaways
- Nvidia G-Sync combats screen tearing and stuttering for a smoother gaming experience with reduced input lag.
- Different G-Sync levels (G-Sync Compatible, G-Sync, G-Sync Ultimate) offer varying features and prices.
- Hardware requirements for G-Sync monitors aren’t restrictive, while the choice between G-Sync and FreeSync depends on personal preference and budget.
Buying gaming hardware is becoming increasingly complicated by the day, so knowing what you’re looking for to cut through the marketing jargon.
When it comes to monitors, there’s more to consider than just resolution, refresh rate, and color accuracy. If you’re looking to combat screen tearing and stuttering issues, you need to know about Nvidia’s G-Sync and what it brings to the table.
What Is Nvidia G-Sync and How Does It Affect Your Games?
Introduced in 2013, Nvidia’s G-Sync technology combats screen tearing and any stuttering issues it may cause. This results in a smoother gaming experience visually and in terms of input lag.
Screen tearing occurs when the game’s refresh rate doesn’t match your monitor’s. This generally happens when the game is running at a higher refresh rate than the monitor, resulting in a buffer of frames waiting to get on your display, causing screen tearing, jitters, and increasing input lag.
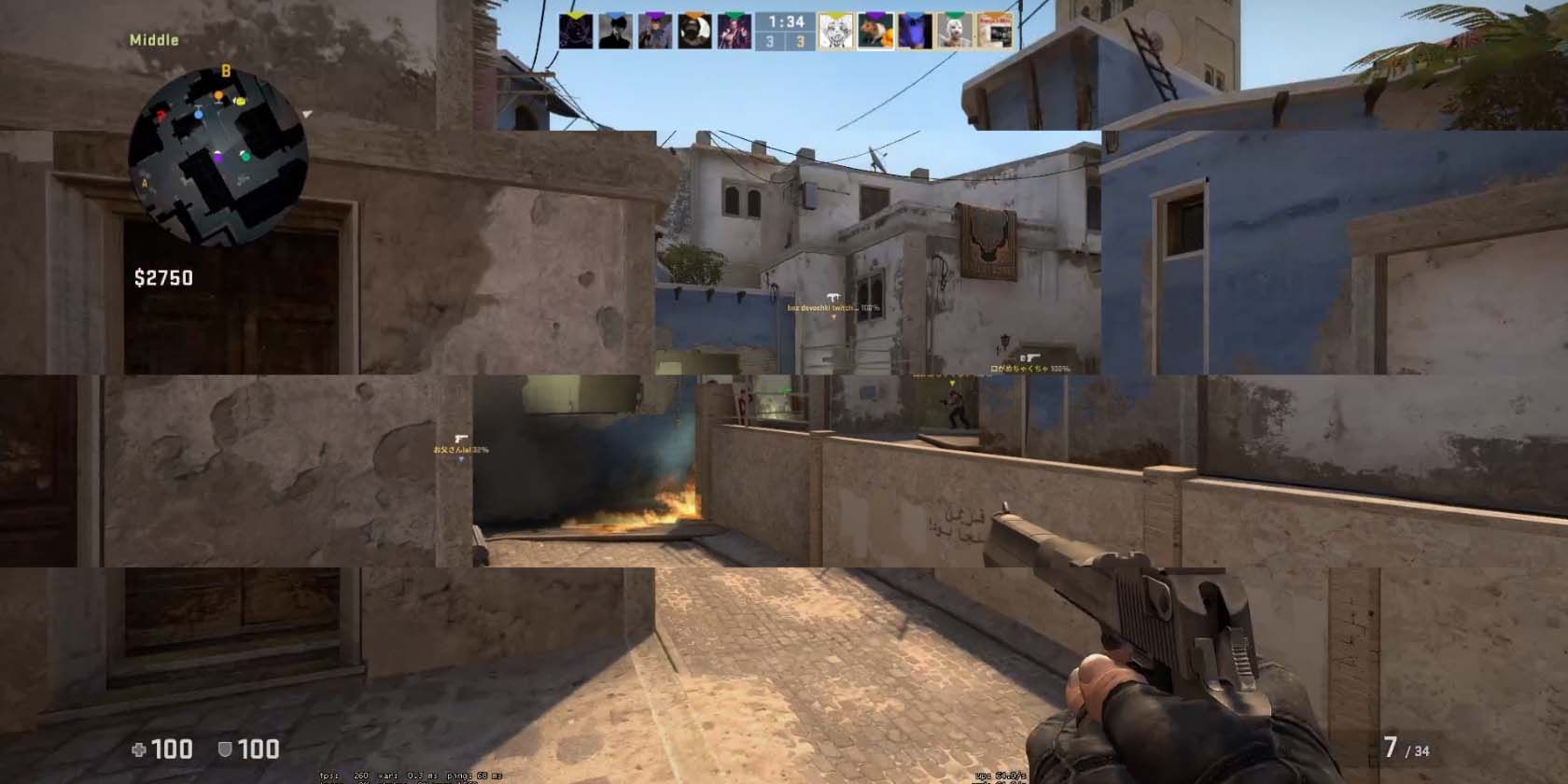
G-Sync combats this by having compatible displays synchronize their minimum and maximum refresh rates using an Nvidia GPU, thanks to its variable refresh rate chip.
This means the GPU only outputs the required amount of frames for the monitor, ensuring they reach the display just when required. Since new frames don’t have to wait before they’re displayed on your monitor, it also helps reduce input lag.
Depending on the type of G-Sync your monitor supports, benefits include the following (in addition to addressing the main issue of screen tearing):
- Lower input lag
- Improved motion clarity
- More realistic color reproduction with smoother gradients
- Realistic brightness and a wider color range
That said, just because your monitor is labeled G-Sync compatible, that doesn’t mean you’re going to get all the benefits Nvidia claims. You might be limited to a handful of features based on your monitor and GPU combination, which is why knowing what kind of G-Sync your monitor and GPU support is important.
Different Types of G-Sync Explained
Since its release, G-Sync has seen several updates and improvements. The technology has branched out into three main categories.
- G-Sync Compatible: These monitors don’t use Nvidia processors for variable refresh rates but have been validated by Nvidia to provide a good variable refresh rate performance.
- G-Sync: The standard G-Sync tier, these monitors use the Nvidia G-Sync processor and have been certified with over 300 tests. It’s also referred to as native G-Sync or true G-Sync.
- G-Sync Ultimate: In addition to using Nvidia processors and certifications, these monitors also provide better HDR, contrast, color reproduction, and lower input latency. It was previously called G-Sync HDR.
As you can probably guess, monitors marked “G-Sync Compatible” are at the bottom and will cost less than their G-Sync and G-Sync Ultimate counterparts as the manufacturers aren’t required to use Nvidia’s proprietary hardware.

Hamlin Rozario/MakeUseOf
That said, Nvidia’s processor allows monitors to use their entire refresh rate range, from 1 Hz to 360 Hz. This provides much better performance compared to G-Sync-compatible monitors, which generally switch between 30, 60, 90, and 144 Hz.
Finally, native G-Sync and G-Sync Ultimate monitors can also work with AMD GPUs. This gives you more GPU options if you’re looking for a switch or upgrade down the line. Alternatively, you can alsoenable Nvidia G-Sync for FreeSync monitors , which is AMD’s response to Nvidia’s anti-screen tearing tech.
Hardware Requirements for G-Sync and G-Sync Ultimate
There are some hardware requirements you need to keep in mind when using these monitors, although these are usually easily met. To use a G-Sync monitor with a desktop, you need a GTX 650 Ti or better GPU connected to the monitor over DisplayPort 1.2 or higher.
Laptops need a GTX 980M, 970M, 965M, or better GPU over the same DisplayPort 1.2 connection. G-Sync compatible monitors also require Nvidia’s R340.52 driver or higher running on Windows 10.
The requirements for G-Sync Ultimate are slightly higher, with laptops and desktops requiring a GTX 1050 or better GPU connected over DisplayPort 1.4 directly from the GPU. You’ll also need the R396 GA2 driver or higher running on Windows 10.
Chances are your computer already meets these requirements, so you’ll mostly have to focus on the monitor itself. Thankfully,Nvidia’s exhaustive list of G-Sync Compatible, native G-Sync, and G-Sync Ultimate monitors will help you choose.
G-Sync vs. FreeSync
Much like their GPU and CPU battles, Nvidia and AMD offer G-Sync and FreeSync, respectively, to provide a tearing and stutter-free gaming experience. While both G-Sync and FreeSync do the same thing, they use different approaches.
Nvidia uses G-Sync processors built into the display to sync framerates.FreeSync, on the other hand, uses the GPU ‘s ability to manage a monitor’s refresh rate using the Adaptive Sync tech built into the Display Port standard.
For this reason, you’ll see a lot more FreeSync displays on the market, priced cheaper than Nvidia-compatible offerings. However, FreeSync monitors also tend to suffer screen ghosting more often.
Should You Buy G-Sync-Compatible Hardware?
If you can afford it, absolutely.
A powerful enough PC will easily be able to push high frames per second in a game. This is especially true if you’re playing competitive first-person shooter or racing games where your game’s frame rate and the monitor’s ability to display them matter a lot.
G-Sync isn’t all for visual appeal, either. As mentioned before, since frames don’t have to wait to be displayed on your monitor, the reduced input latency can make your games feel more responsive, potentially impacting performance.
However, don’t expect your gaming performance to skyrocket just because you bought a G-Sync monitor. Your game will almost certainly look better and feel faster, but that isn’t a replacement for skill.
Also read:
- [New] In 2024, Exclusive MP4 Uploader to Facebook Platform
- [New] Pioneering the Future Workplace Through Virtual Tech
- Direct Xbox Control Over Windows - A Step-by-Step Guide (142 Chars)
- Efficient Methods to Solve Steam Buys Glitch
- Google Play Pass: The Epitome of Greatness with One Irk
- How To Bypass Google FRP on Oppo K11x
- How to Unlock Realme GT 5 Pro PIN Code/Pattern Lock/Password
- Nvidia's Advancement in Graphics: DLSS 3.5 Explained
- Premier Tech Showcase - IFA 2023 Edition
- Rust Development Secrets: Overcoming Freeze Problems with New Techniques
- Sprinkle Some Smiles Emojis on YouTube for 2024
- The Best Xbox Capture Cards
- Ultimate Guide to Enhancing Videos by Efficiently Changing Their Bitrates for Performance
- Title: Enhance Your Gameplay with the Seamless Magic of Nvidia G-Sync
- Author: William
- Created at : 2024-12-28 13:35:12
- Updated at : 2025-01-03 16:32:15
- Link: https://games-able.techidaily.com/enhance-your-gameplay-with-the-seamless-magic-of-nvidia-g-sync/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.